What Are Forex And Cfds
This is a guide to "CFD trading for beginners". In this article, you lot will learn which financial instruments are available to merchandise in the CFD market. We will show y'all why you should consider CFDs as role of your trading strategy by examining their advantages. When you lot are ready to kickoff trading CFDs, check out our list of the best CFD brokers .
Contracts for Deviation (CFDs) have been around since the early 2000s, and their use by hedge funds and private traders has grown exponentially. Originally created for institutional players that wanted a flexible, leveraged product that would allow them to hedge their portfolios while avoiding British postage duty, CFDs in Forex and in other non-Forex assets chop-chop gained traction in the retail market as well. But what are CFDs exactly? Why practise brokers seem to be continuously enhancing their product offering with more CFDs? Why and when should a trader prefer to trade CFDs rather than trade in stocks, futures or rolling spot Forex? Welcome to our guide to CFD trading for beginners.
What is a Contract for Deviation?
Starting right from the basics, CFD stands for "Contract for Difference". Understanding CFDs is quite simple:
-
A CFD is a contract which you tin can buy (or sell) at 1 price and sell (or buy back) at another.
-
The cost movements of a CFD mimic any underlying security they are based on (Indices, Shares, Commodities, Forex, etc).
-
Your profit or loss will depend on the difference of the buy and sell price.
In other words, a CFD gives you the right to own the price difference between the opening and closing price of your merchandise, which is why information technology is a "Contract for Deviation" later all. Nonetheless, you do not actually own the underlying security, which is the difference between trading a CFD and investing.
For example, here is a chart of the "real" Dow Jones Futures (via TradingView) from February 2021 to March 13th, 2021.
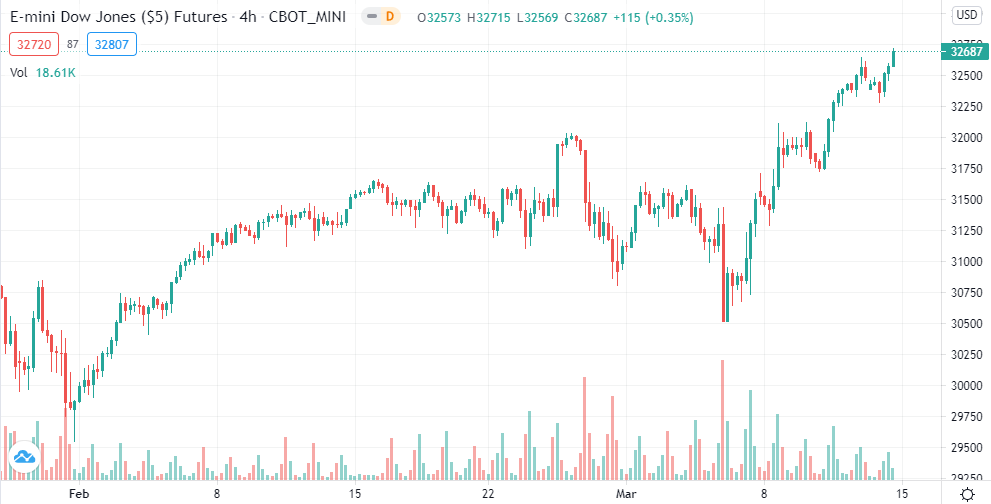
And hither is the Dow Jones CFD nautical chart, every bit offered past a regulated broker.
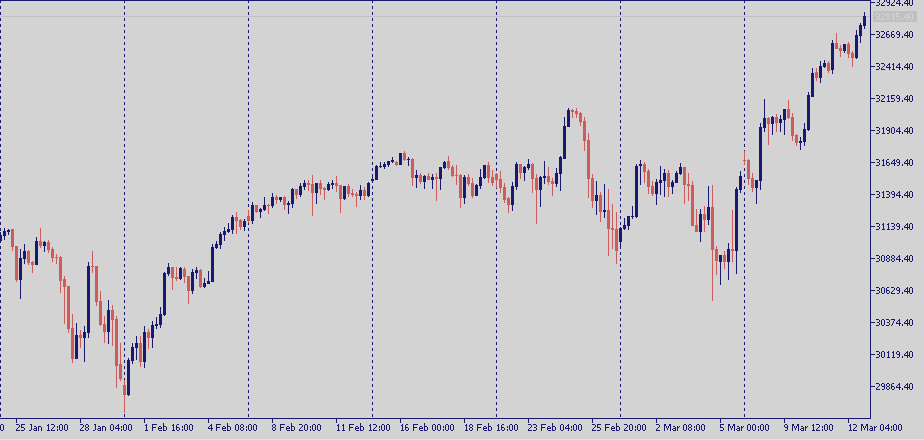
Clearly, the CFD chart is a faithful replica of the real Dow Jones Futures.
Pros and Cons of CFDs
Pros
-
A vast universe of instruments to trade including shares, indices, commodities, and currency pairs.
-
The high degree of leverage bachelor ways you take small margin requirements, making CFD trading highly efficient.
-
Yous can short CFDs without having to go through the intricacies of traditional short selling.
-
CFDs are exempt from postage stamp duty (in the U.K.).
-
You can deduct your losses from profits for tax purposes (in the U.K.).
Cons
-
Yous can lose more than your initial deposit.
-
When used improperly, leverage can magnify losses and then be sure to use solid coin and trade direction strategies to insulate your business relationship from big losses.
-
Trading CFDs profitably requires skill and experience. Get to know the intricacies of the instruments you are trading and consider trading with a demo account for some fourth dimension before risking whatsoever existent money.
-
Any positions left open overnight are subject area to funding fees.
-
CFD profits are subject to capital gains revenue enhancement (in the U.Yard.).
Types of CFDs
CFDs are available on a huge range of assets including global indices, stocks, currencies, commodities. Therefore, past trading CFDs you can diversify your positions which ways that your range of opportunities increases exponentially compared to a trader that but focuses on ane asset course such as Forex, for example.
Let us examine the main differences between CFDs and other financial instruments.
CFDs vs. Forex: like Forex, CFDs are OTC (over the counter) products (and then there is no key exchange) and if you lot have a position with a CFD you do not physically own the underlying asset. Whether y'all purchase EUR/USD or the South&P 500 Index CFD, you are just taking an educated bet on the possible short-term price movement. Yet, whereas all currency prices are driven by geopolitical events (Brexit, Coronavirus), economic information (inflation, GDP, employment) and interest rates (yields), CFDs can differ. The price oscillations of a CFD depend on the underlying musical instrument. A CFD based on WTI Crude Oil volition motion depending on the demand/supply characteristics of the oil marketplace; a CFD on the S&P 500 Index volition be more often than not dependant on global growth prospects; a CFD on a single stock like Tesla will be dependant on specific news relative to renewable free energy, tweets past Elon Musk, earnings prospects, growth prospects, and the company'south regulatory environment.
CFDs vs. Futures: CFDs and futures are both derivative products that are based on an underlying asset. You can go long or short in both CFDs and futures. The chief differences betwixt CFDs and futures contracts are the contract size and margin requirements. CFDs allow much more flexibility and tin can be traded with smaller business relationship sizes considering of the granularity of their pricing structure and leverage. Yet CFDs are likewise simpler: while futures have death dates, CFDs do not. Too, CFDs do not require physical delivery. Imagine trading WTI Crude Oil futures and forgetting to whorl the position over: y'all would be answerable to take physical delivery of the number of barrels you lot were trading. This cannot happen when trading CFDs, because you do not physically ain any of the underlying asset.
CFDs vs. Commodities: "fewer headaches" is how we tin describe CFD trading every bit opposed to traditional commodity trading. CFD traders need not worry about physical delivery, contract expiry, or lot sizes. As such, when trading CFDs on coffee, crude oil, wheat, copper etc., y'all just demand to focus on your pre-trade analysis, trade execution and merchandise management. Your trading is much more than efficient and much less circuitous.
CFDs vs. Stocks: whether to trade physical shares or CFDs boils downwardly to capital availability and objectives. For example, when trading stocks you pay the full value of your stocks upfront, whereas the leverage bachelor on CFDs make them a more efficient musical instrument to use. Nevertheless, on CFDs your losses tin exceed your initial deposit, whereas in stocks yous can only lose the amount you invested. Nevertheless, stocks have limitations on short selling, whereas CFDs let you lot to trade either long or short without whatever restrictions. Stock trading is limited to the open up hours of the relevant stock commutation, while CFDs can be traded effectually the clock subject to your broker'southward market place hours. Ultimately, stock trading is perhaps ameliorate suited for longer-term objectives because at that place is no fourth dimension-based fee incurred to continue trades open, whereas there is a cost to holding CFDs overnight (every bit described previously). Therefore, CFDs are more directed towards intraday and swing trading, whereas stocks are more suited for long-term investing.
CFDs vs ETFs: this is a more interesting comparison considering CFDs and ETFs are both speculations on the motion of the underlying musical instrument (in neither case does the merchandise own the underlying instrument). All the same, ETFs are perhaps more than useful for longer term strategies (similar stocks) whereas CFDs are more useful for curt-term strategies. ETFs are quoted on public stock exchanges and tin can represent entire sectors, industries, commodity baskets, and every bit such tin can offering internal diversification benefits while maintaining low costs. The closest match to CFDs are alphabetize ETFs (like Dax or S&P 500 ETFs). But even hither at that place are differences: with ETFs you lot must pay the full price of your underlying asset, whereas the leverage available on CFDs make them more than efficient to utilise. With ETFs y'all can never lose more than your initial investment, while with CFDs y'all can. ETFs are non subject to rollover fees, whereas CFDs are. As such, ETFs are best used for longer-term strategies like dollar-cost averaging, asset allocation, and gamble-parity; CFDs are best used for brusque-term directional trading. Happily, several Forex brokers now offer CFDs on more popular ETFs, pregnant that traders can perform ETF CFD trading and benefit from exposure to ETFs in CFD format.
CFDs vs Options: options are perhaps a more than efficient fashion to merchandise stocks due to the fact they accept embedded leverage (1 option typically allows yous to control 100 shares of a visitor) but the benefit might cease at that place. Similar CFDs, options are derivative instruments that motion based on the direction, volatility, and liquidity of the underlying security, likewise every bit the time to death. Options have an expiry date then have something in common with commodity futures. Only options are certainly more complex to understand due to the multiple variables that impact their price. Also, options are near entirely directed at stocks whereas brokers take created CFDs on many different asset classes.
What is CFD Trading?
CFDs trading is a course of leveraged trading, where the broker allows you to control a large position with a relatively pocket-sized amount of money (this small amount of money is margin). The leverage can of course piece of work for you lot or confronting you because your turn a profit and loss is dependent on the notional value of the position y'all control, and then the best illustration requires working through an example to empathize what this means in practical terms.
An Instance of a CFD Trade
Allow u.s. look at an example of a transaction.
Most brokers offer "micro-size" positions in CFDs, then even clients with very small accounts can take a CFD position based on their views.
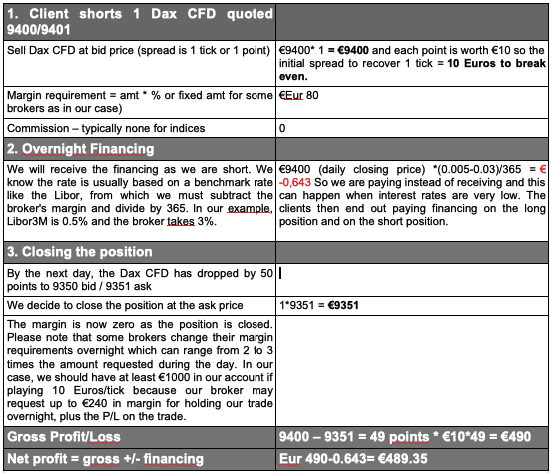
Every bit you can run across, in this (realistic) case, we have gained more than the margin required to brand the trade. We could have easily lost more than the margin requested for the position. In this sense, CFDs are high leverage products. The financing cost seems very depression at this bespeak, but we are in a moment of depression interest rates. In these moments, Issuers gain marginally less on their financing haircut BUT they go to accuse clients on both the long AND the short positions.
Now for some other example, with a 5-twenty-four hour period holding period. Observe how much financing tin impact the end profit, even in a low-charge per unit environment.
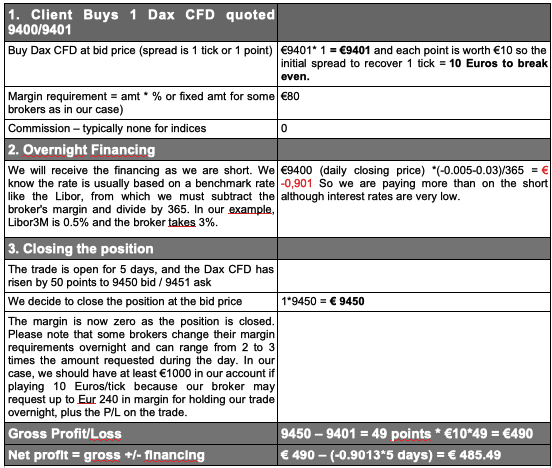
What are we trying to illustrate? Simply that CFDs tin get expensive, especially if you are on the incorrect side of the market. Just without even considering the uncertain outcome of any given bet, let the states explore the costs, in terms of volatility (measured by the average true range indicator) of trading a CFD on the Dax Index.
The Dax normally moves with relatively high volatility. Hence, there is much opportunity hither for profit or loss. At present, we have been in an extended depression-charge per unit environment, and so for simplicity nosotros tin considering the same (extremely low) financing cost seen in the example in a higher place, or $0.90 per twenty-four hour period. We have taken the average true range of the Dax in low volatility and college volatility environments.
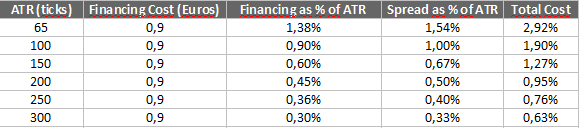
When interest rates finally offset to rise, the financing costs volition rise in lockstep. So, CFDs are brusque term trading vehicles, because over the long term, the financing cost will significantly bear upon your P/L.
This is the principal divergence between CFD trading and investing. It is inefficient to use CFDs for long-term positions. Instead, CFDs are best used for intraday and brusque-term positions.
How to Merchandise CFDs
Most retail traders are familiar with Forex trading strategies. As noted to a higher place, currency prices are driven by geopolitical events (Brexit, Coronavirus), economical data (inflation, Gross domestic product, employment) and involvement rates (yields). The cost oscillations of a CFD depend on the underlying musical instrument. So, information technology is worth looking at the fundamental influences that touch on different kinds of CFDs:
-
Index CFDs
-
Crude Oil CFD
-
Gold CFD
-
Industrial Metallic CFDs
How to Merchandise Stock Index CFDs: Growth is Key
Since they represent a grouping of stocks, all index CFDs follow the aforementioned dynamics and since the earth is now more interconnected than always before, nigh stock index CFDs are strongly correlated as the chart beneath shows.
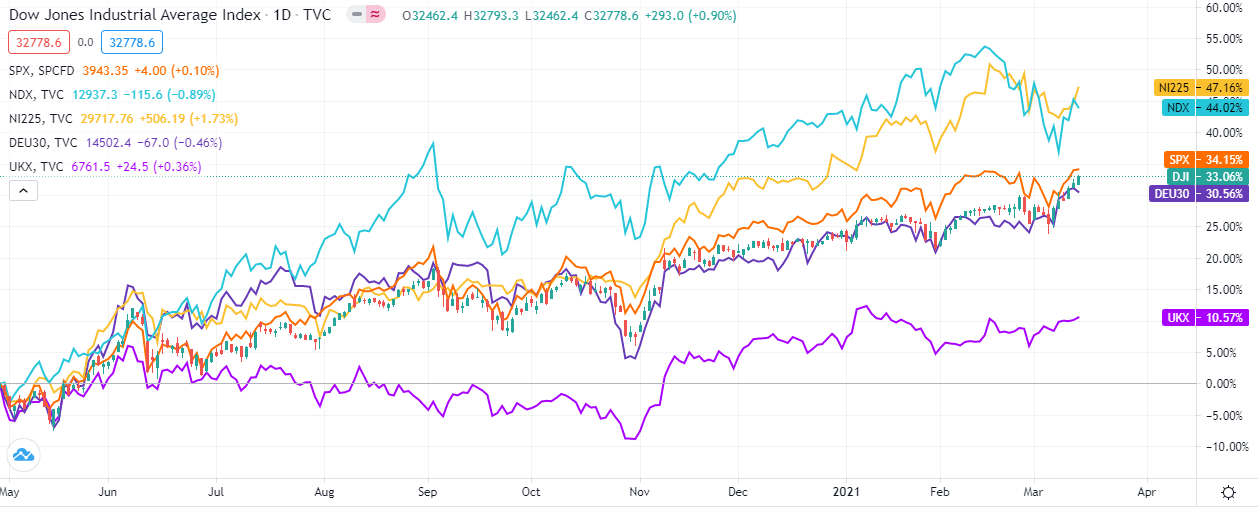
Major Stock Indices 2020-2021
Mathematically, we can carve up all stock cost changes into just two categories:
ane. A stock'due south cost can alter considering its multiple(southward) change. This means that stock traders change their view of what a stock is worth without any underlying change in the stocks accomplished revenues or earnings. For example, the (trailing) P/E ratio or multiple changes, or the cost to volume value ratio changes. Generally, this means that the outlook for time to come earnings has get more than positive or more negative or the required rate of return on the stock has changed. Multiple changes are responsible for near all minute-to infinitesimal, movement in stock prices.
2. A stock's fundamentals change due to the release of new fiscal information. For example, the stock's book value, abaft 12 months acquirement or trailing 12 calendar month'southward earnings changes when information technology releases financial performance for the latest quarter. Fundamental growth is responsible for most of the long-term change in a stock's price over a menses of years.
At present, since Alphabetize CFDs are a weighted average of stock prices, we know what makes them tick: growth! Earnings are the cornerstone of stock assay and Indices also take their ain earnings figures. When the economy is doing well, companies are producing and selling their goods/services and thus the forecast for future earnings is good.
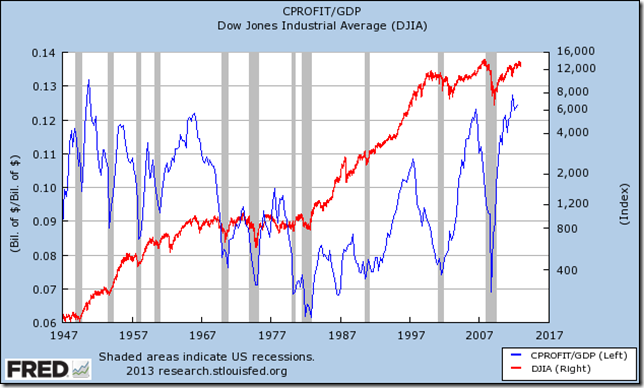
Correlation Corporate Profits and the Dow Jones Index
Vice-versa: when things start to wait gloomy, when the consumer is non purchasing or when there is some perception of emerging risk, the outlook for the future is not and then sure or positive. Having a good grip on the fundamentals of the US economy (for the Dow), the German economy (for the Dax), the Canadian economy (for the TSX) and so on, is the only thing you lot – as a trader – demand to understand the oscillations in toll of an Index CFD. If everything is based on growth, and then the resolving question is: how is the economy doing, and how are the emerging information prints plumbing equipment into the current context?
How to Trade Rough Oil CFDs
Here are the main drivers to pay attention to, to sympathize how and why the toll of Crude Oil moves. Remember, prices move because market participants shift their expectations for the underlying asset and these expectations are based on emerging fundamentals, not charts alone.
-
Risk Appetite and Supply Side Shocks. As is the instance for most growth-sensitive commodities, Crude Oil is influenced by risk appetite, over and above the prevailing balance of supply and need. When general supply/need dynamics are driving price, the correlation between EIA/API Inventories and Rough is axiomatic. When risk is the driver, the correlation between Crude, the VIX alphabetize and the DOW becomes more than evident.
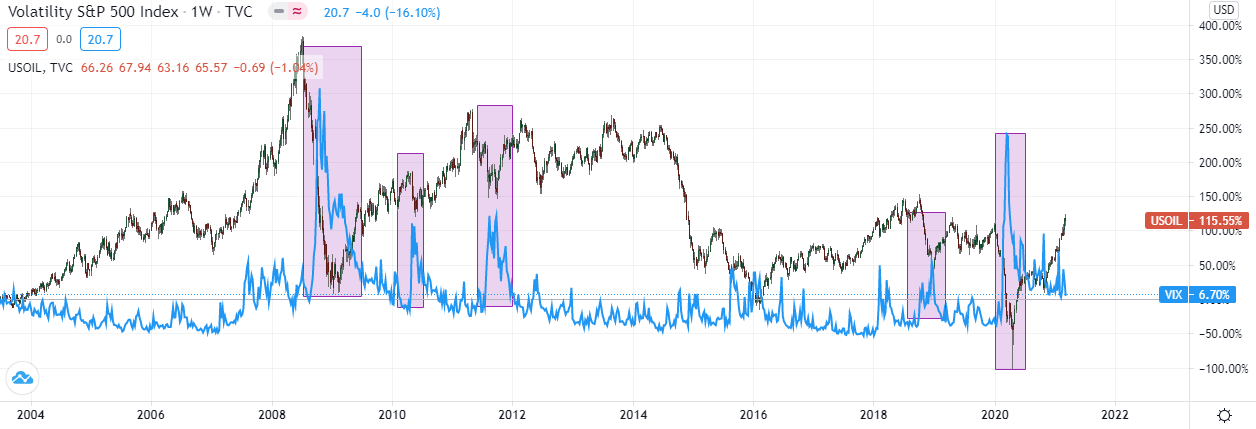
Vix Alphabetize (Blue) vs. Crude (Green & Cerise) – Weekly View
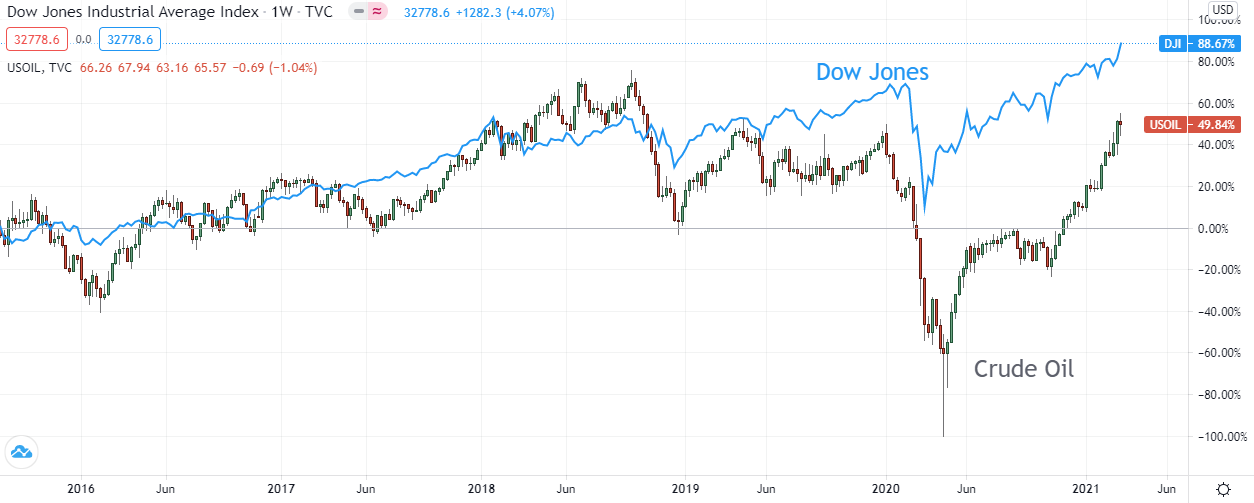
Dow (Blue) vs. Crude (Red & Green) – Weekly View
-
The EIA Rough Oil Stocks Change (which is issued every Wednesday) actually is the nearly important data print. It is a weekly mensurate of the change in the number of barrels in stock of crude oil and its derivates and tends to generate large cost volatility as oil prices touch worldwide economies. In Forex, these dynamics can have an impact on commodity related currencies such as the Canadian dollar.
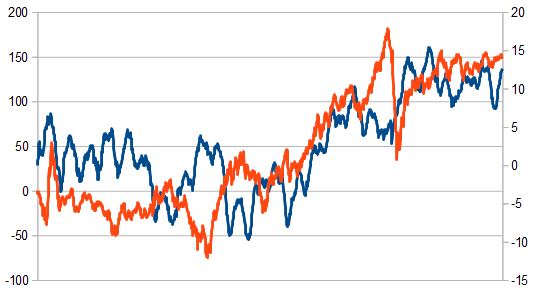
Inventories Week to Week %-change (blue, lhs) vs. Crude %-alter (orangish, rhs)
-
The API Weekly Crude Oil Stock (issued on Tuesday evenings) have become a piddling more popular recently merely are by and large less followed than official EIA information. The American Petroleum Institute attempts to anticipate official EIA data and equally such has validity.
How to Merchandise Gilt and Metal CFDs
Gold really is the male monarch of all commodities. Empathise Gold, and you can sympathise all other precious metals. Gold tends to have an affect on other precious metals like Silver and Platinum, dictating their price, and more so with Silver because Platinum is more than oriented towards industrial use.
There are 4 main reasons that make Gold the about important precious metal in the earth:
-
Central Banks hold large amounts of Gold as part of their official reserves and buy & sell big amounts of the metal based on their time to come expectations for the economy.
-
In times of gamble aversion, traders and investors shift capital away from risky assets and search for security in Gold equally highlighted by the chart below.
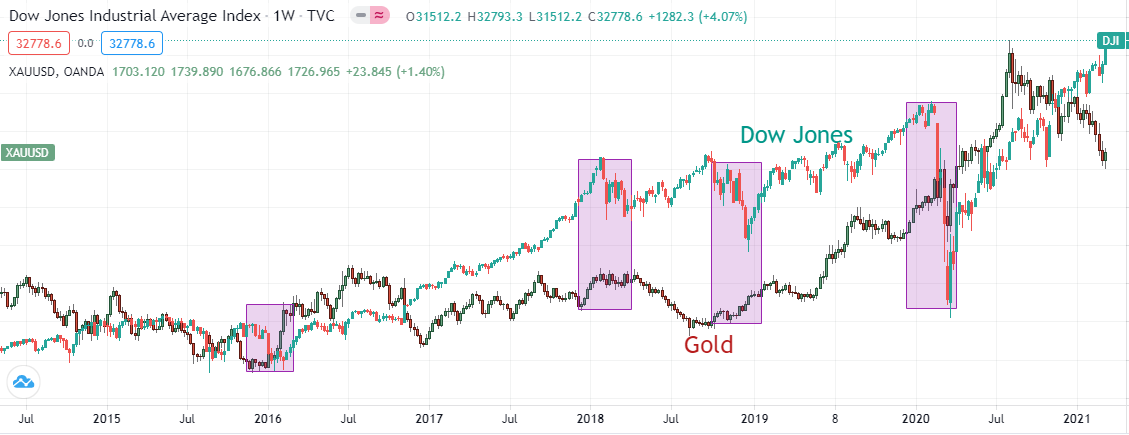
Gold vs Dow Jones Index 2014-2021
-
USD trends bear on Aureate since the metallic is primarily priced in USD per ounce, so naturally lower USD prices tend to increase the relative value of Golden (and vice versa) as highlighted by the chart beneath.
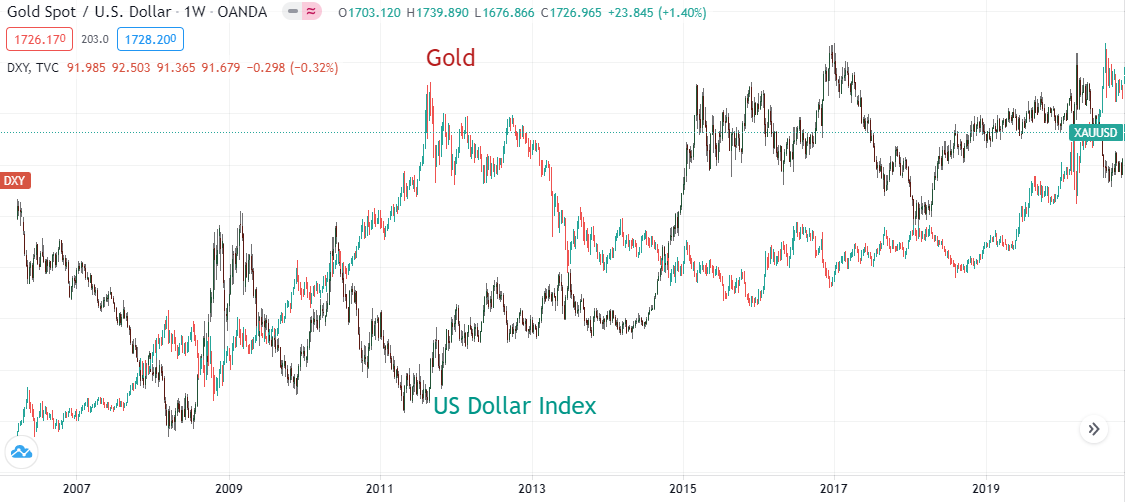
Gold vs United states of america Dollar Index 2014-2021
-
Inflation trends as well affect the demand for Gilt, since the precious metal is seen as a hedge confronting inflation.
Silverish CFDs
It might be interesting to know that Silver has a huge array of industrial uses, since information technology is used as electrical components in computers and household appliances such as washing machines. Information technology too has less conventional uses, such equally in photograph evolution and in odour control in shoes and apparel. It is also more commonly existence used in trace amounts in bandages and is still used in X-rays.
Merely for day-to-day trading, one chart says it all:
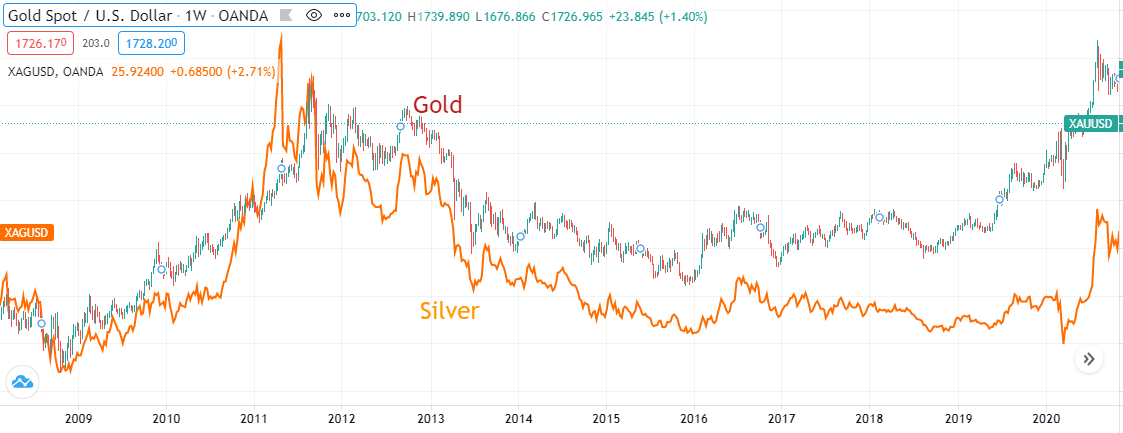
Gold vs Silver 2008-2021
Argent tracks Golden. The cost dynamics are very much the same, albeit with different volatility characteristics. Hence, for trading objectives, Gold remains more highly-seasoned given the higher volatility.
Platinum and Palladium
Palladium has a broad multifariousness of uses, and thus appears several consumer and business organisation market. Despite being a precious metal, Palladium tends to rail the stock market. Its industrial uses tend to overshadow its status as a rare metal. So, ane of the best ways to use Palladium charts is to spread information technology against Gold. This shows how well the industrial (real) economy is doing and the Palladium/Golden spread will plow bearish rapidly when the economy starts to deadening down. On the one mitt you have diminished demand for consumer products which impacts the need for Palladium. On the other hand, yous have a tendential flight to safe.
 Palladium/Golden spread vs. Dow Jones Index
Palladium/Golden spread vs. Dow Jones Index
Platinum is also a rare metal and is used for jewellery. However, merely similar Palladium, information technology has industrial uses that overshadow its status as a rare metallic. Platinum is used in the automotive industry, and in the medicinal manufacture. Again, Platinum trades like Palladium only it tends to be more sensitive to economic shocks. Platinum's spread against Aureate is a much improve indicator of what market place participants think about the future prospect for the economy.
Copper is yet another industrial metal with demand/supply characteristics that are much more like Palladium and Platinum than Gold or Silver. Being a skilful heat conductor, it has a broad range of uses in the construction, electronics, and transportation industries. So economical growth prospects are normally the strongest commuter of copper prices, alongside USD dynamics. As well, the demand for copper is highly correlated with the economic growth prospects of Mainland china and India.
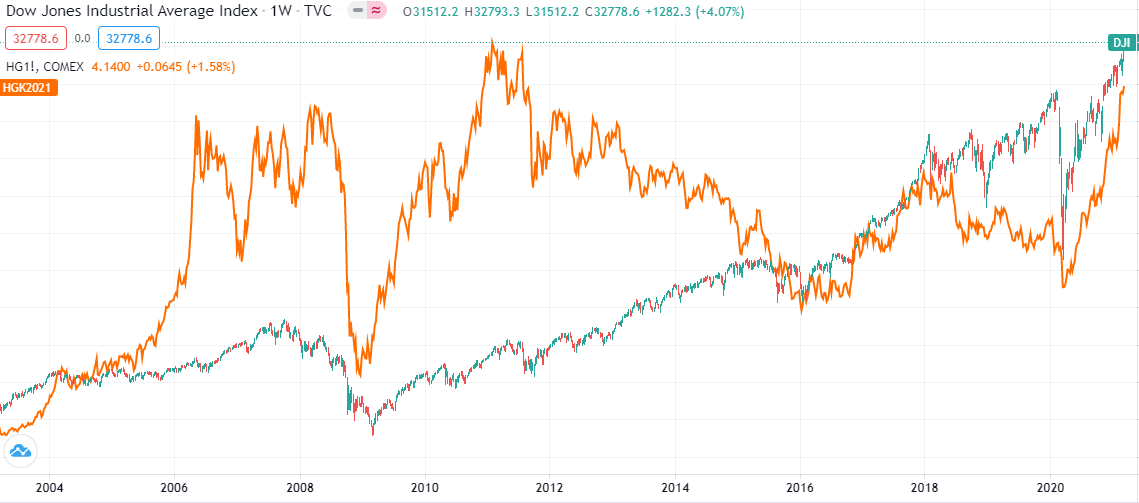
Copper (Orange) vs. Dow Jones Index
How is a CFD Quoted?
Many traders are confused by the departure between the actual Futures price and the CFD quote. To make matters more confusing, each banker basically has a different quote for the same production. The reason why CFDs "rails" the underlying instrument but accept a different quote lies in the calculations made to "create" the CFD in the first place:
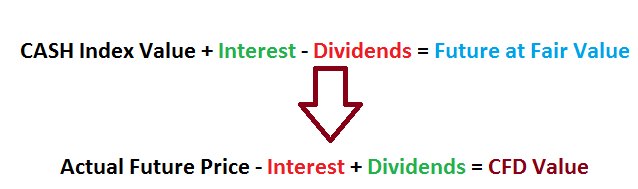
For the finance geeks that really want to understand a CFD's pricing construction, let u.s.a. get technical for a moment.
If the CFD Price = PT and the toll of the Underlying = UT, when a trader and his broker become into a CFD trade at fourth dimension t, the condition must be that:
-
For each moment in time prior to the close of the merchandise (T) the cash flows betwixt parties are as follows: the heir-apparent of the CFD must pay the seller involvement of r*U t-1 (contract rate of interest per mean solar day, applied at rollover time) and the seller must pay the buyer any dividends D t
-
At time T (the close of the position) there is a cash menses of P T - P t = U T - P t
So, the CFD pricing mechanism that keeps the CFD price locked to the underlying cost, and that as well satisfies futures pricing equations, is:
P T-1 = F T-1 – (U T-one *(e r -1)) + D T = U T-ane
This is the financing cost (contract interest) justified by the fact that the CFD issuer (i.east. the banker) should take a concrete position in the underlying, for which it has set aside margin, and is non creating CFDs for free.
The explicit financing calculation is usually expressed as follows:
Financing = (amt*shut*rate)/365
Where:
amt = Trade Size
close = daily endmost price of the CFD contract
rate = relevant 3Month LIBOR rate (usually), to which the CFD issuers commonly add (for long positions) or deduct (for short positions) a certain amount. For example, if your banker adds 3% to longs and deducts 3% for shorts, so effectively their haircut is 6% (considering they make you lot pay 3% on the longs and they give you iii% less on the shorts).
We should try to understand a lilliputian more what the pricing formula means:
-
Long one CFD = P T-1 = F T-1 – (U T-1 *(due east r -1)) + D T and then the client benefits from (positive) future price variation and the dividends and pays Libor 3M+3% (in our case).
-
Short one CFD = - P T-1 = - F T-1 + (U T-1 *(due east r -i)) – D T then the client benefits from (negative) future price variation and Libor 3M-3% (in our example) and pays the dividends.
Why is information technology beneficial for a CFD issuer (a CFD banker) to offer as many CFDs every bit they maybe tin can?
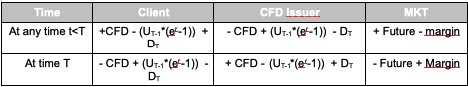
The to a higher place example is a case of the CFD issuer acting as a DMA issuer (non a Market Maker) and hedging its CFD exposure in the market with the underlying future. So, the issuer is acting in the most transparent way possible, eliminating whatever potential conflicts of interest. It seems all the terms abolish themselves out (without transaction costs, obviously) merely brokers exercise not offer CFDs for free. So where is the benefit?
The do good is in the financing term! In our example, the market rate at which the issuer can transact is Libor3M, while it charges the client 3% on the long side and deducts 3% from the involvement that the client would otherwise benefit from on the brusque side. The total haircut that the issuer (in our example) is receiving is half-dozen%. In fact, it is likely that the issuer benefits from at least 2*Libor applied to the client. Yet that the issuer too benefits from the spread information technology applies which is much wider in percentage terms than the spread applied to the underlying stock or hereafter.
In obviously English, here is the simplified explanation:
-
Financing costs are where your broker will make money, above and beyond the spread y'all pay to brand the transaction.
-
Financing costs are loftier and generally deplete the profit obtained on trades that final more than a couple of weeks.
-
Information technology follows that CFD trading is directed at short term forays into the market and is non advisable as a vehicle for position trading.
-
CFDs will e'er track the underlying market, considering how they are built and quoted.
Last Thoughts
CFDs are a flexible, leveraged, brusk-term trading instrument. The benefit of CFDs is that traders can merchandise a vast assortment of different instruments via CFDs, since brokers nowadays create CFDs on practically all nugget classes (stocks, forex, commodities, indices, metals, bonds). However, traders need to have a firm grasp of take a chance direction and coin management principles to properly trade CFDs while avoiding margin calls.
FAQs
Is CFD Trading Profitable?
CFDs are merely an instrument that allows you to take a stance (bullish or bearish) on a given fiscal asset. As such, to exist profitable you lot must possess solid trading skills. Also, the high caste of leverage available with CFDs means yous need to take a firm grasp of coin management and trade management practices to be assisting.
Some mutual mistakes you want to avoid:
Non having a solid trading system when trading CFDs.
Property onto losing positions, hoping they will get up.
Getting into a position based on somebody else'southward idea.
Increasing your position size after a loss, hoping to make back previous loses.
How Exercise I First Trading CFDs?
When you first CFD trading equally a beginner, you should starting time consider opening a CFD demo account with a regulated broker where you tin can practice trading in a adventure-free environment. Once you have become familiar with CFDs, you can:
-
open up a live trading business relationship with a regulated broker,
-
choose the instrument yous want to trade,
-
enter a merchandise size,
-
execute the club,
-
monitor/manage your trade,
-
close the position.
Why are CFDs Illegal?
CFDs are not currently allowed in the USA due to restrictions imposed past the South.E.C. due to the fact they are OCT (over the counter) financial instruments and are heavily regulated.
Is CFD Trading Safe?
CFDs are a leveraged financial product, and every bit such should be treated similarly to other leveraged products. CFDs accept been traditionally used by sophisticated traders to have advantage of opportunistic, brusk-term positions in the markets. Retail traders are lured towards CFDs because of the capacity to brand large profits from small moves on the underlying instrument (be it an alphabetize, a stock, a currency pair, a commodity, etc). This is due to leverage: the fact that brokers crave for example ten% margin (so you lot only need $100 to control a notional value of $1000).
To sum upwards, there is null inherently unsafe about CFDs.
Source: https://www.dailyforex.com/forex-articles/2015/03/forex-cfds-etfs-what-are-they/42979
Posted by: gintherskillart.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Are Forex And Cfds"
Post a Comment